Repost from FracTracker
[Editor: Although the Map of CA Crude by Rail Terminals needs to be updated with information about Valero Benicia’s proposed crude by rail terminal, this is a highly recommended, carefully researched report out of the Center for Science, Technology and Society, Drexel University. – RS]
CA Refineries: Sources of Oil and Crude-by-Rail Terminals
By Kyle Ferrar and Kirk Jalbert, May 23, 2016![]() Refineries in California plan to increase capacity and refine more Bakken Shale crude oil and Canadian tar sands bitumen. However, CA’s refinery communities that already bear a disparate amount of the burden (the refinery corridor along the north shore of the East Bay) will be more impacted than they were previously. New crude-by-rail terminals will put additional Californians at risk of accidents such as spills, derailments, and explosions. Additionally, air quality in refinery communities will be further degraded as refineries change to lower quality sources of crude oil. Below we discuss where the raw crude oil originates, why people are concerned about crude-by-rail projects, and what CA communities are doing to protect themselves. We also discuss our GIS analysis, showing the number of Californians living within the half-mile blast zones of the rail lines that currently are or will be supported by the new and existing crude by rail terminal projects.
Refineries in California plan to increase capacity and refine more Bakken Shale crude oil and Canadian tar sands bitumen. However, CA’s refinery communities that already bear a disparate amount of the burden (the refinery corridor along the north shore of the East Bay) will be more impacted than they were previously. New crude-by-rail terminals will put additional Californians at risk of accidents such as spills, derailments, and explosions. Additionally, air quality in refinery communities will be further degraded as refineries change to lower quality sources of crude oil. Below we discuss where the raw crude oil originates, why people are concerned about crude-by-rail projects, and what CA communities are doing to protect themselves. We also discuss our GIS analysis, showing the number of Californians living within the half-mile blast zones of the rail lines that currently are or will be supported by the new and existing crude by rail terminal projects.
Sources of Raw Crude Oil
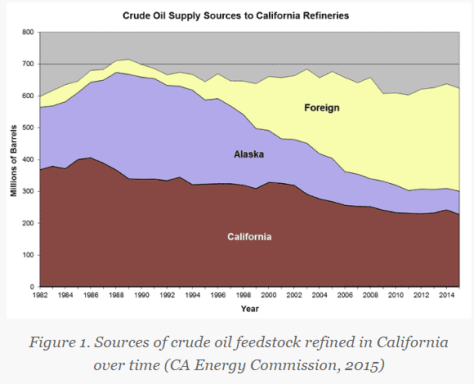
Predictions project that sources of raw crude oil are shifting to the energy intensive Bakken formation and Canadian Tar Sands. The Borealis Centre estimates an 800% increase of tar sands oil in CA refineries over the next 25 years (NRDC, 2015). The increase in raw material from these isolated locations means new routes are necessary to transport the crude to refineries. New pipelines and crude-by-rail facilities would be necessary, specifically in locations where there are not marine terminals such as the Central Valley and Central Coast of CA. The cheapest way for operators in the Canadian Tar Sands and North Dakota’s Bakken Shale to get their raw crude to CA’s refinery markets is by railroad (30% less than shipping by marine routes from ports in Oregon and Washington), but this process also presents several issues.California’s once plentiful oil reserves of locally extracted crude are dwindling and nearing depletion. Since 1985, crude extraction in CA has dropped by half. Production from Alaska has dropped even more, from 2 million B/D (barrels per day) to around 500,000 B/D. The 1.9 million B/D refining capacity in CA is looking for new sources of fuels. Refineries continue to supplement crude feedstock with oil from other sources, and the majority has been coming from overseas, specifically Iraq and Saudi Arabia. This trend is shown in figure 1:
CA Crude by Rail
More than 1 million children — 250,000 in the East Bay — attend school within one mile of a current or proposed oil train line (CBD, 2015). Using this “oil train blast zone” map developed by ForestEthics (now called Stand) you can explore the various areas at risk in the US if there was an oil train explosion along a rail line. Unfortunately, there are environmental injustices that exist for communities living along the rail lines that would be transporting the crude according to another ForestEthics report.
To better understand this issue, last year we published an analysis of rail lines known to be used for transporting crude along with the locations of oil train incidents and accidents in California. This year we have updated the rail lines in the map below to focus on the Burlington Northern Santa Fe (BNSF) and Union Pacific (UP) railroad lines, which will be the predominant lines used for crude-by-rail transport and are also the focus of the CA Emergency Management Agency’s Oil by Rail hazard map.
The specific focus of the map in Figure 2 is the five proposed and eight existing crude-by-rail terminals that allow oil rail cars to unload at the refineries. The eight existing rail terminals have a combined capacity of 496,000 barrels. Combined, the 15 terminals would increase CA’s crude imports to over 1 million B/D by rail. The currently active terminals are shown with red markers. Proposed terminals are shown with orange markers, and inactive terminals with yellow markers. Much of the data on terminals was taken from the Oil Change International Crude by Rail Map, which covers the entire U.S.
Figure 2. Map of CA Crude by Rail Terminals
View Map Fullscreen | How Our Maps Work | Download Rail Terminal Map Data
Additional Proposals
The same type of facility is currently operating in the East Bay’s refinery corridor in Richmond, CA. The Kinder Morgan Richmond terminal was repurposed from handling ethanol to crude oil, but with no public notice. The terminal began operating without conducting an Environmental Impact Report (EIR) or public review of the permit. Unfortunately, this anti-transparent process was similar to a tactic used by another facility in Kern County. The relatively new (November 2014) terminal in Taft, CA operated by Plains All American Pipeline LLC also did not conduct an EIR, and the permit is being challenged on the grounds of not following the CA Environmental Quality Act (CEQA).
EIRs are an important component of the permitting process for any hydrocarbon-related facility. In April 2015 in Pittsburg, for example, a proposed 50,000 B/D terminal at the WesPac Midstream LLC’s railyard was abandoned due to community resistance and criticism over the EIR from the State Attorney General, along with the larger proposal of a 192,000 B/D marine terminal.
Still, many other proposals are in the works for this region. Targa Resources, a midstream logistics company, has a proposed a 70,000 B/D facility in the Port of Stockton, CA. Alon USA has a permitted project for revitalizing an idle Bakersfield refinery because of poor economics and have a permit to construct a two-unit train/day (150,000 B/D) offloading facility on the refinery property. Valero dropped previous plans for a rail oil terminal at its Wilmington refinery in the Los Angeles/Long Beach port area, and Questar Pipeline has preliminary plans for a rail oil terminal in the desert east of the Palm Springs area for a unit-train/day.
Air Quality Impacts of Refining Tar Sands Oil
Crude-by-rail terminals bring with them not only the threat of derailments and the risk of other such accidents, but the terminals are also a source of air emissions. Terminals – both rail and marine – are major sources of PAH’s (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons). The Sacramento Valley Railroad (SAV) Patriot rail oil terminal at a business park on the former McClellan Air Force Base property actually had its operating permit withdrawn by Sacramento air quality regulators due to this issue (read more). The terminal was unloading and reloading oil tanker cars.
FracTracker’s recent report, Emissions in the Refinery Corridor, shows that the refineries in this region are the major point source for emissions of both cancer and non-cancer risk drivers in the region. These air pollution sources get worse, however. According to the report by NRDC, changing the source of crude feedstock to increased amounts of Canadian Tar Sands oil and Bakken Shale oil would:
… increase the levels of highly toxic fugitive emissions; heavy emissions of particulate, metals, and benzene; result in a higher risk of refinery accidents; and the accumulation of petroleum coke* (a coal-like, dusty byproduct of heavy oil refining linked to severe respiratory impacts). This possibility would exacerbate the harmful health effects faced by the thousands of low-income families that currently live around the edges of California’s refineries. These effects are likely to include harmful impacts to eyes, skin, and the nervous and respiratory systems. Read NRDC Report
Petroleum coke (petcoke) is a waste product of refining tar sands bitumen (oil), and will burden the communities near the refineries that process tar sands oil. Petcoke has recently been identified as amajor source of exposures to carcinogenic PAH’s in Alberta Canada (Zhang et al., 2016). For more information about the contributions of petcoke to poor air quality and climate change, read this report by Oil Change International.
The contribution to climate change from accessing the tar sands also needs to be considered. Extracting tar sands is estimated to release on average 17% average more green-house gas (GHG) emissions than conventional oil extraction operations in the U.S., according to the U.S. Department of State. (Greenhouse gases are gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to climate change on a global scale.) The refining process, too, has a larger environmental / public health footprint; refining the tar sands to produce gasoline or diesel generates an average of 81% more GHGs (U.S. Dept of State. Appendix W. 2015). In total this results in a much larger climate impact (NRDC, NextGen Climate, Forest Ethics. 2015).
Local Fights
People opposed to CA crude by rail have been fighting the railway terminal proposals on several fronts. In Benicia, Valero’s proposal for a rail terminal was denied by the city’s Planning Commission, and the project’s environmental impact report was denied, as well. The city of Benicia, however, hired lawyers to ensure that the railway projects are built. The legality of railway development is protected regardless of the impacts of what the rails may be used to ship. This legal principle is referred to as “preemption,” which means the federal permitting prevents state or local actions from trying to limit or block development. In this case, community and environmental advocacy groups such as Communities for a Better Environment, the Natural Resources Defense Council, and the Stanford-Mills Law Project all agree the “preemption” doctrine doesn’t apply here. They believe preemption does not disallow the city or other local governments from blocking land use permits for the refinery expansion and crude terminals that unload the train cars at the refinery.
The fight for local communities along the rail-lines is more complicated when the refinery is far way, under the jurisdiction of other municipalities. Such is the case for the Phillips 66 Santa Maria Refinery, located on California State Highway 1 on the Nipomo Mesa. The Santa Maria refinery is requesting land use permits to extend track to the Union Pacific Railway that transits CA’s central coast. The extension is necessary to bring the rail cars to the proposed rail terminal. This project would not just increase traffic within San Luis Obispo, but for the entirety of the rail line, which passes directly through the East Bay. The project would mean an 80-car train carrying 2 million gallons of Bakken Crude would travel through the East Bay from Richmond through Berekely and Emeryville to Jack London Square and then south through Oakland and the South Bay. This would occur 3 to 5 times per week. In San Luis Obispo county 88,377 people live within the half-mile blast zone of the railroad tracks.
In January, the San Luis Obispo County Planning Department proposed to deny Phillips 66 the permits necessary for the rail spur and terminals. This decision was not easy, as Phillips 66, a corporation ranked Number 7 on the Fortune 500 list, has fought the decision. The discussion remained open with many days of meetings, but the majority of the San Luis Obispo Planning Commission spoke in favor of the proposal at a meeting Monday, May 16. There is overwhelming opposition to the rail spur project coming from 250 miles away in Berkeley, CA. In 2014, the Berkeley and Richmond city councils voted to oppose all transport of crude oil through the East Bay. Without the rail spur approval, Phillips 66 declared the Santa Maria refinery would otherwise transport oil from Kern County via 100 trucks per day. Learn more about this project.
GIS Analysis
GIS techniques were used to estimate the number of Californians living in the half mile “at risk” blast zone in the communities hosting the crude-by-rail lines. First, we estimated the total population of Californians living a half mile from the BNSF and UP rail lines that could potentially transport crude trains. Next, we limited our study area to just the East Bay refinery corridor, which included Contra Costa and the city of Benicia in Solano County. Then, we estimated the number of Californians that would be living near rail lines if the Phillips 66 Santa Maria refinery crude by rail project is approved and becomes operational. The results are shown below:
- Population living within a half mile of rail lines throughout all of California: 6,900,000
- Population living within a half mile of rail lines in CA’s East Bay refinery communities: 198,000
- Population living within a half mile of rail lines along the UP lines connecting Richmond, CA to the Phillips 66 Santa Maria refinery: 930,000
CA Crude by Rail References
- NRDC. 2015. Next Frontier for Dangerous Tar Sands Cargo:California. Accessed 4/15/16.
- Oil Change International. 2015. Rail Map.
- Global Community Monitor. 2014. Community Protest Against Crude Oil by Rail Blocks Entrance to Kinder Morgan Rail Yard in Richmond
- CEC. 2015. Sources of Oil to California Refineries. California Energy Commission. Accessed 4/15/16.
- Zhang Y, Shotyk W, Zaccone C, Noernberg T, Pelletier R, Bicalho B, Froese DG, Davies L, and Martin JW. 2016. Airborne Petcoke Dust is a Major Source of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region. Environmental Science and Technology. 50 (4), pp 1711–1720.
- U.S. Dept of State. 2015. Final Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement for Keystone XL Pipeline. Accessed 5/15/16.
- U.S. Dept of State. 2015. Appendix W Environmental Impact Statement for Keystone XL Pipeline Appendix W. Accessed 5/15/16.
- NRDC, NextGen Climate, Forest Ethics. 2015. West Coast Tar Sands Invasion. NRDC 2015. Accessed 4/15/16.
** Feature image of the protest at the Richmond Chevron Refinery courtesy of Global Community Monitor.






You must be logged in to post a comment.